Rostro‐caudal organization of the human posterior superior temporal sulcus revealed by connectivity profiles
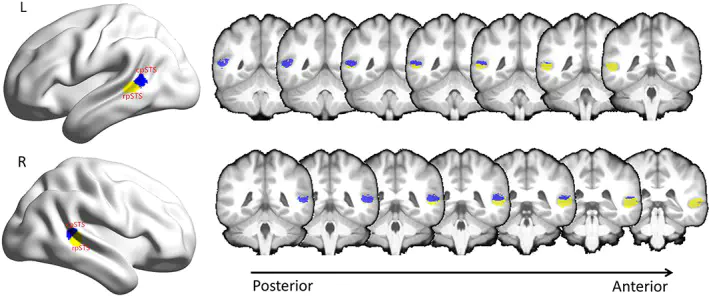 pSTS parcellation
pSTS parcellationAbstract
The posterior superior temporal sulcus (pSTS) plays an important role in biological motion perception but is also thought to be essential for speech and facial processing. However, although there are many previous investigations of distinct functional modules within the pSTS, the functional organization of the pSTS in its full functional heterogeneity has not yet been established. Here we applied a connectivity-based parcellation strategy to delineate the human pSTS subregions based on distinct anatomical connectivity profiles and divided it into rostral and caudal subregions using diffusion tensor imaging. Subsequent multimodal connection pattern analyses revealed distinct subregional connectivity profiles. From this we inferred that the two subregions are involved in distinct functional circuits, the language processing loop and the cognition attention network. These results indicate a convergent functional architecture of the pSTS that can be revealed based on different types of connectivity and is reflected in different functions and interactions. In addition, when the subregions were performing their processing in the different functional circuits, we found asymmetry in the bilateral pSTS. Our findings may improve the understanding of the functional organization of the pSTS and provide new insights into its interactions and integration of information at the subregional level.