 Asymmetries
AsymmetriesAbstract
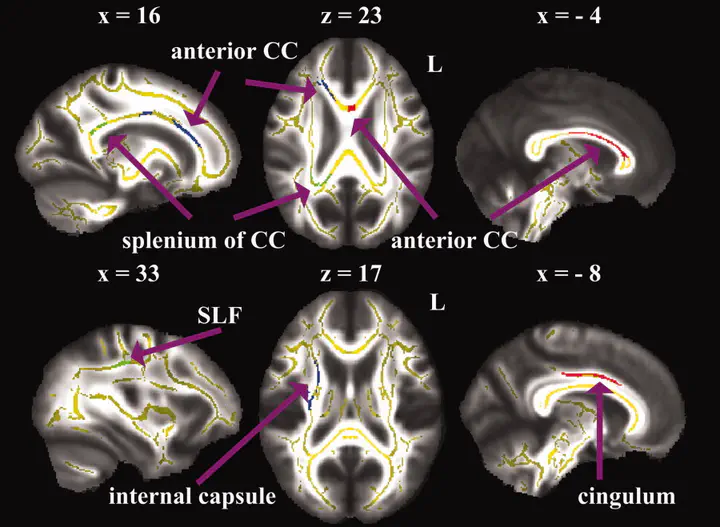
White matter (WM) asymmetries of the human brain have been well documented using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). However, the relationship between WM asymmetry pattern and cognitive performance is poorly understood. By means of tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS) and voxel-based analyses of whole brain, this study examined the WM asymmetries and the correlations between WM integrity/asymmetries and three distinct components of attention, namely alerting, orienting, and executive control (EC), which were assessed by attention network test (ANT). We revealed a number of WM anisotropy asymmetries, including leftward asymmetry of cingulum, corticospinal tract and cerebral peduncle, rightward asymmetry of internal capsule, superior longitudinal fasciculus and posterior corona radiata, as well as heterogeneous asymmetries in anterior corpus callosum and anterior corona radiata (ACR). Moreover, specific correlation was found between asymmetric pattern of inferior frontal ACR and EC performance. Additionally, this study also proposed that there were no significant relationships of WM anisotropy asymmetries to alerting and orienting functions. Further clusters of interest analyses and probabilistic fiber tracking validated our findings. In conclusion, there are a number of differences in WM integrity between human brain hemispheres. Specially, the anisotropy asymmetry in inferior frontal ACR plays a crucial role in EC function. Our finding is supportive of the functional studies of inferior frontal regions and in keeping with the theory of the brain lateralization on human ventral attention system.